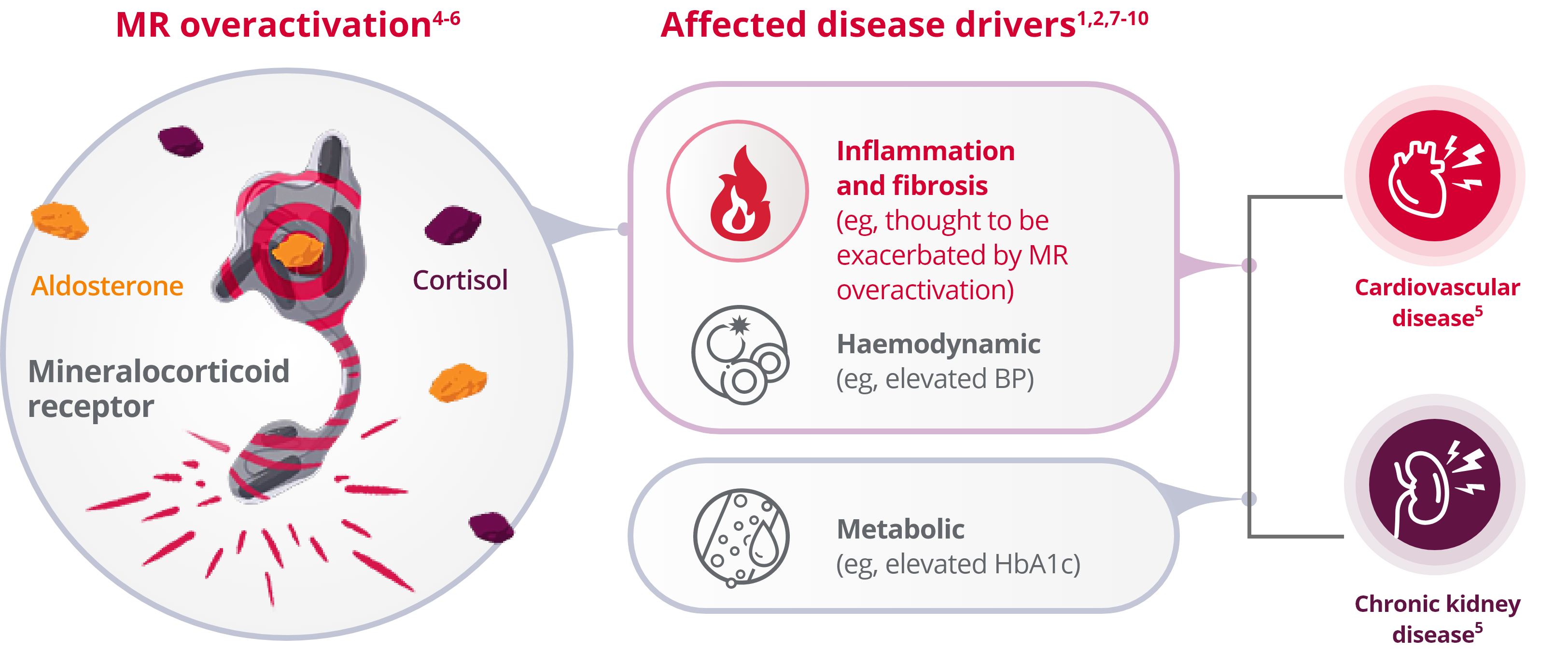
Despite standard of care, a key risk factor remains largely unaddressed in patients with CKD and T2D1-3

MR overactivation contributes to several pathophysiological mechanisms including5:
- Sodium retention
- Extracellular matrix remodeling and hypertrophy
- Inflammation and fibrosis
Your patients need protection against MR overactivation
Firialta is the first and only selective MRA approved to treat CKD and T2D6
With no affinity to other hormone receptors, Firialta selectively blocks6,11:
- MR overactivation
- MR-mediated sodium reabsorption
- Expression of pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic mediators
Firialta selectively and potently blocks MR overactivation in the heart and kidneys11
Selected characteristics of 2 classes of MRAs12-14
Characteristic
Potency to MR*
Nonsteroidal Firialta
High
Spironolactone
High
Eplerenone
Low
Selectivity to MR*
Nonsteroidal Firialta
High
Spironolactone
Low
Eplerenone
Medium
Metabolites*
Nonsteroidal Firialta
No active metabolites
Spironolactone
Multiple active metabolites
Eplerenone
No active metabolites
Half-life
Nonsteroidal Firialta
Short half-life
(~2 to 3 hours)
(~2 to 3 hours)
Spironolactone
Long half-life
(>20 hours)
(>20 hours)
Eplerenone
Moderate half-life
(4 to 6 hours)
(4 to 6 hours)
Distribution (rodent model)
Nonsteroidal Firialta
Balanced between kidney and heart
Spironolactone
Kidney > heart
(≥6-fold)
(≥6-fold)
Eplerenone
Kidney > heart
(~3-fold)
(~3-fold)
Risk of hyperkalaemia
Nonsteroidal Firialta Spironolactone
Finerenone was associated with lower rates of hyperkalaemia than spironolactone in the phase 2 trial ARTS
Eplerenone
No head-to-head data exist
Effects on blood pressure
Nonsteroidal Firialta Spironolactone
Finerenone was associated with less reduction of SBP compared with spironolactone in the phase 2 trial ARTS
Eplerenone
No head-to-head data exist
Firialta is indicated for the treatment of chronic kidney disease (with albuminuria) associated with Type 2 Diabetes in adults.
*Based on preclinical animal models. The clinical consequences of these characteristics are unknown.17
BP=blood pressure; CKD=chronic kidney disease; CV=cardiovascular; eGFR=estimated glomerular filtration rate; ESKD=end-stage kidney disease; HbA1c=glycated haemoglobin; HF=heart failure; MI=myocardial infarction; MR=mineralocorticoid receptor; MRA=mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; SBP=systolic blood pressure; T2D=type 2 diabetes.
References:
- Alicic RZ, et al. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018;25(2):181-191. doi:10.1053/j.ackd.2017.12.002. Return to content
- Alicic RZ, et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;12(12):2032–2045. Return to content
- Bakris GL, et al; FIDELIO-DKD Investigators. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(23):2219-2229. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2025845. Return to content
- Bauersachs J, et al. Hypertension. 2015;65(2):257-263. Return to content
- Kolkhof P, et al. Pharmacol Res. 2021;172:1-13. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105859. Return to content
- Firialta (SmPC). Return to content
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Diabetes Work Group. Kidney Int. 2020;98(4S):S1-S115. Return to content
- Toth-Manikowski S, et al. J Diabetes Res. 2015;2015. doi:10.11552015/697010. Return to content
- Black LM, et al. J Histochem Cytochem. 2019;67(9):663-681. doi:10.1369/0022155419852932. Return to content
- Tesch GH, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:313. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00313. Return to content
- Firialta Local Product Information, BPOM 2023. Return to content
- Kintscher U, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2022;179:3220–3234. Return to content
- Kolkhof P, et al. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017;243:271-305. doi:10.1007/164_2016_76. Return to content
- Pitt B, et al. Eur Heart J. 2013;34(31):2453-63. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/eht187. Return to content
- Spironolactone Local Product Information, BPOM 2022. Return to content
- INSPRA (eplerenone) [prescribing information]. New York, NY: Pfizer; August 2020. Return to content
- Fagart J, et al. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(39)-29932-29940. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.131342. Epub 2010 Jul 22. Return to content